(クイックリファレンス)
4 コマンドライン
Authors: Graeme Rocher, Peter Ledbrook, Marc Palmer, Jeff Brown, Luke Daley, Burt Beckwith ,
Japanese Translation: T.Yamamoto, Japanese Grails Doc Translating Team
このドキュメントの内容はスナップショットバージョンを元に意訳されているため、一部現行バージョンでは未対応の機能もあります。
Version: 2.1.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT
4 コマンドライン
Grails' command line system is built on
Gant - a simple Groovy wrapper around
Apache Ant.
Grailsのコマンドラインシステムは
Gant(シンプルな
Apache AntのGroovyによるラッパー)によって構築されています。
However, Grails takes it further through the use of convention and the grails command. When you type:
Grailsでは
grailsコマンドを使用し、Gantとは少し違った実行方法になります。
Grails searches in the following directories for Gant scripts to execute:
このように入力した場合、GrailsはGantスクリプトを実行するために以下のディレクトリを探しに行きます。
USER_HOME/.grails/scriptsPROJECT_HOME/scriptsPROJECT_HOME/plugins/*/scriptsGRAILS_HOME/scripts
Grails will also convert command names that are in lower case form such as run-app into camel case. So typing
Grailsは "run-app" のような小文字のコマンドをキャメルケースに変換して探します。なので次のように入力すると:
Results in a search for the following files:
結果、以下のファイルを検索するよう指定したことになります。
USER_HOME/.grails/scripts/RunApp.groovyPROJECT_HOME/scripts/RunApp.groovyPLUGINS_HOME/*/scripts/RunApp.groovyGLOBAL_PLUGINS_HOME/*/scripts/RunApp.groovyGRAILS_HOME/scripts/RunApp.groovy
If multiple matches are found Grails will give you a choice of which one to execute.
もし、複数の結果が見つかった場合はGrailsはどれを実行するかの選択肢を提示してきます。
When Grails executes a Gant script, it invokes the "default" target defined in that script. If there is no default, Grails will quit with an error.
GrailsがGantスクリプトを実行するとき、デフォルトとして設定されたターゲットを起動します。デフォルト指定(setDefaultTarget(main)など)がない場合、Grailsはエラーで終了します。
To get a list of all commands and some help about the available commands type:
実行可能なコマンドのヘルプとリストを表示したい場合は以下を入力します:
which outputs usage instructions and the list of commands Grails is aware of:
このように入力すると、Grailsが認識しているコマンドのリストと使用方法が出力されます:
Usage (optionals marked with *):
grails [environment]* [target] [arguments]*Examples:
grails dev run-app
grails create-app booksAvailable Targets (type grails help 'target-name' for more info):
grails bootstrap
grails bug-report
grails clean
grails compile
...
Refer to the Command Line reference in the Quick Reference menu of the reference guide for more information about individual commands
左メニューにある個別のコマンドラインリファレンス情報も参照して下さい。
It's often useful to provide custom arguments to the JVM when running Grails commands, in particular with
run-app where you may for example want to set a higher maximum heap size. The Grails command will use any JVM options provided in the general
JAVA_OPTS environment variable, but you can also specify a Grails-specific environment variable too:
export GRAILS_OPTS="-Xmx1G -Xms256m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m"
grails run-app
non-interactive mode
When you run a script manually and it prompts you for information, you can answer the questions and continue running the script. But when you run a script as part of an automated process, for example a continuous integration build server, there's no way to "answer" the questions. So you can pass the
--non-interactive switch to the script command to tell Grails to accept the default answer for any questions, for example whether to install a missing plugin.
For example:
grails war --non-interactive
4.1 インタラクティブモード
Interactive mode is the a feature of the Grails command line which keeps the JVM running and allows for quicker execution of commands. To activate interactive mode type 'grails' at the command line and then use TAB completion to get a list of commands:
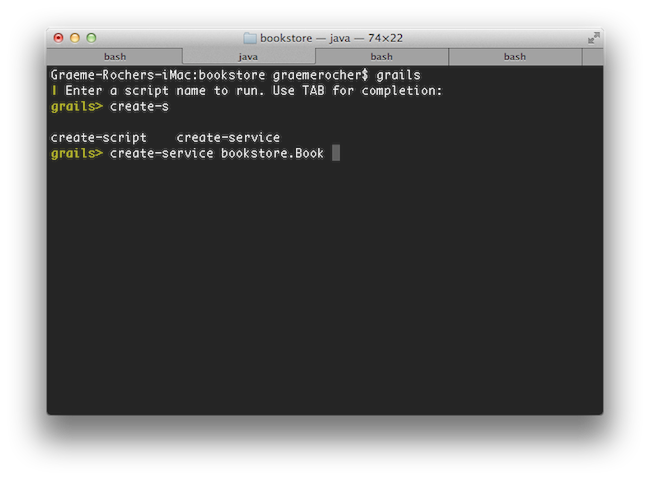
If you need to open a file whilst within interactive mode you can use the
open command which will TAB complete file paths:
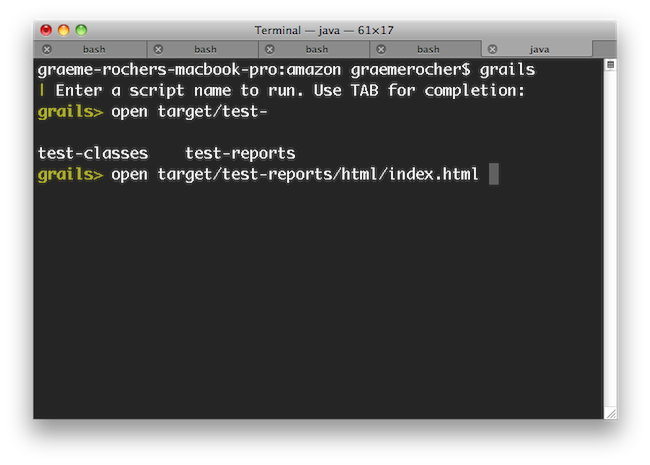
Even better, the
open command understands the logical aliases 'test-report' and 'dep-report', which will open the most recent test and dependency reports respectively. In other words, to open the test report in a browser simply execute
open test-report. You can event open multiple files at once:
open test-report test/unit/MyTests.groovy will open the HTML test report in your browser and the
MyTests.groovy source file in your text editor.
TAB completion also works for class names after the
create-* commands:
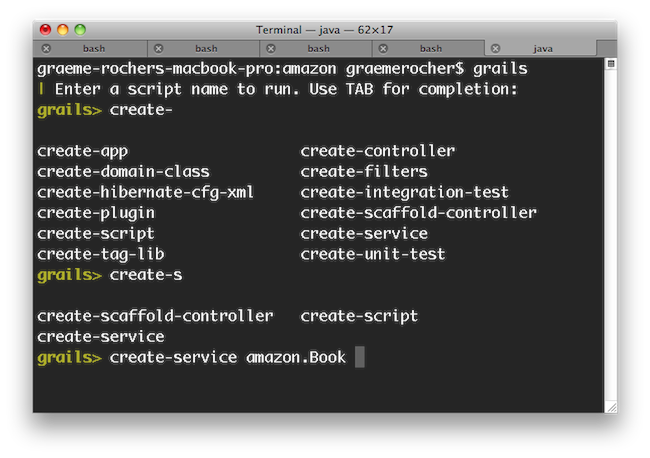
If you need to run an external process whilst interactive mode is running you can do so by starting the command with a !:
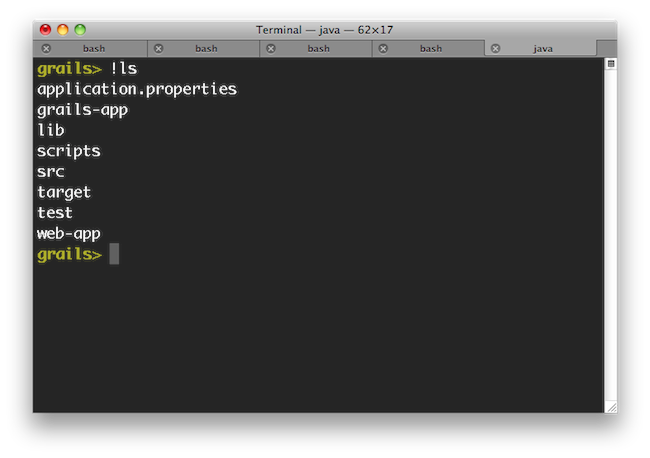
Note that with ! (bang) commands, you get file path auto completion - ideal for external commands that operate on the file system such as 'ls', 'cat', 'git', etc.
4.2 Gantスクリプトの作成
You can create your own Gant scripts by running the
create-script command from the root of your project. For example the following command:
プロジェクトのルートディレクトリで
create-scriptコマンドを実行することにより、自分でGantスクリプトを作成することができます。例えば以下のようなコマンドです:
grails create-script compile-sources
Will create a script called scripts/CompileSources.groovy. A Gant script itself is similar to a regular Groovy script except that it supports the concept of "targets" and dependencies between them:
このコマンドにより
scripts/CompileSources.groovyというスクリプトが作成されます。Gantスクリプト自身は通常のGroovyスクリプトと似ていますが、ターゲットという概念とそれぞれのターゲットの依存関係をサポートしています。
target(default:"The default target is the one that gets executed by Grails") {
depends(clean, compile)
}target(clean:"Clean out things") {
ant.delete(dir:"output")
}target(compile:"Compile some sources") {
ant.mkdir(dir:"mkdir")
ant.javac(srcdir:"src/java", destdir:"output")
}
As demonstrated in the script above, there is an implicit
ant variable (an instance of
groovy.util.AntBuilder) that allows access to the
Apache Ant API.
上記で示したスクリプトのように、暗黙的な変数のantは
Apache Ant APIを使うことができます。
In previous versions of Grails (1.0.3 and below), the variable was Ant, i.e. with a capital first letter.
前バージョンのGrails(1.0.3以前)では、変数名はAntのように大文字始まりでした。
You can also "depend" on other targets using the depends method demonstrated in the default target above.
また、上記のdefaultターゲットで示したように、
dependsメソッドを使って他のターゲットに 依存させることができます。
デフォルトターゲット
The default target
In the example above, we specified a target with the explicit name "default". This is one way of defining the default target for a script. An alternative approach is to use the setDefaultTarget() method:
上記の例では"default"と明示的にターゲットを指定しました。これは、スクリプトでデフォルトターゲットを定義する方法の一つです。(最新のバージョンでは使用できません)代わりに
setDefaultTarget()メソッドを使用することもできます。
target("clean-compile": "Performs a clean compilation on the app source") {
depends(clean, compile)
}target(clean:"Clean out things") {
ant.delete(dir:"output")
}target(compile:"Compile some sources") {
ant.mkdir(dir:"mkdir")
ant.javac(srcdir:"src/java", destdir:"output")
}setDefaultTarget("clean-compile")This lets you call the default target directly from other scripts if you wish. Also, although we have put the call to setDefaultTarget() at the end of the script in this example, it can go anywhere as long as it comes after the target it refers to ("clean-compile" in this case).
こうすることで、他のスクリプトのターゲットを直接デフォルトターゲットに指定できます。
setDefaultTarget()は、対象のターゲット(今回の場合は "clean-compile")の後であればどこにでも書くことができます。
Which approach is better? To be honest, you can use whichever you prefer - there don't seem to be any major advantages in either case. One thing we would say is that if you want to allow other scripts to call your "default" target, you should move it into a shared script that doesn't have a default target at all. We'll talk some more about this in the next section.
どちらのアプローチが良いのでしょうか?正直なところ、あなたは好みで使い分けて使用することができます。どちらの場合も、王道の利点があるわけではありません。一つ言えることは、他のスクリプトからデフォルトターゲットを呼び出せるようにしたい場合は、デフォルトターゲットを持っていない共有スクリプトにそれを移動する必要があるということです。これについては次のセクションでも詳しく説明します。
4.3 Grailsスクリプトの再利用
Grails ships with a lot of command line functionality out of the box that you may find useful in your own scripts (See the command line reference in the reference guide for info on all the commands). Of particular use are the
compile,
package and
bootstrap scripts.
Grailsは独自のスクリプトでも使用できる便利なコマンドライン機能を提供しています(コマンドに関する詳細はリファレンスガイド内のコマンドラインリファレンスを参照してください)。特に
compile、
packageおよび
bootstrapスクリプトはよく利用されます。
The
bootstrap script for example lets you bootstrap a Spring
ApplicationContext instance to get access to the data source and so on (the integration tests use this):
スクリプトはデータソースなどを参照可能にするSpringの
ApplicationContextインスタンスを生成します。(統合テストはこの機能を使っています):
includeTargets << grailsScript("_GrailsBootstrap")target ('default': "Database stuff") {
depends(configureProxy, packageApp, classpath, loadApp, configureApp) Connection c
try {
c = appCtx.getBean('dataSource').getConnection()
// do something with connection
}
finally {
c?.close()
}
}他のスクリプトからターゲットを取り出す
Pulling in targets from other scripts
Gant lets you pull in all targets (except "default") from another Gant script. You can then depend upon or invoke those targets as if they had been defined in the current script. The mechanism for doing this is the includeTargets property. Simply "append" a file or class to it using the left-shift operator:
Gantはターゲットを他のGantスクリプトから取り込むことができます。取り込んだターゲットは、あたかも現在のスクリプトで定義されているかのように実行することができます。この仕組みは
includeTargetsプロパティにより実現されます。単純に左シフト演算子でファイル又は使用するクラスを追加します:
includeTargets << new File("/path/to/my/script.groovy")
includeTargets << gant.tools.IvyDon't worry too much about the syntax using a class, it's quite specialised. If you're interested, look into the Gant documentation.
クラスを使用している構文はGantのルールに従って記述されたクラスを使用しています。もし興味があればGantのドキュメントを参照して下さい。
Core Grailsターゲット
Core Grails targets
As you saw in the example at the beginning of this section, you use neither the File- nor the class-based syntax for includeTargets when including core Grails targets. Instead, you should use the special grailsScript() method that is provided by the Grails command launcher (note that this is not available in normal Gant scripts, just Grails ones).
この章の冒頭の例でお見せしたように、Core Grailsターゲットを含める際に利用する
includeTargetsでは、ファイルベース構文、クラスベース構文のどちらも使用しません。代わりに、Grailsコマンドランチャが提供している
grailsScript()という特別なメソッドを使用します(このメソッドはGrails専用であり、通常のGantでは利用できません)。
The syntax for the grailsScript() method is pretty straightforward: simply pass it the name of the Grails script to include, without any path information. Here is a list of Grails scripts that you could reuse:
grailsScript()メソッドの構文は、単に含めたいGrailsスクリプトの名称を渡すだけです。以下に再利用できるGrailsスクリプトの一覧を示します:
| Script | Description |
|---|
| _GrailsSettings | You really should include this! Fortunately, it is included automatically by all other Grails scripts except _GrailsProxy, so you usually don't have to include it explicitly. |
| _GrailsEvents | Include this to fire events. Adds an event(String eventName, List args) method. Again, included by almost all other Grails scripts. |
| _GrailsClasspath | Configures compilation, test, and runtime classpaths. If you want to use or play with them, include this script. Again, included by almost all other Grails scripts. |
| _GrailsProxy | If you don't have direct access to the internet and use a proxy, include this script to configure access through your proxy. |
| _GrailsArgParsing | Provides a parseArguments target that does what it says on the tin: parses the arguments provided by the user when they run your script. Adds them to the argsMap property. |
| _GrailsTest | Contains all the shared test code. Useful if you want to add any extra tests. |
| _GrailsRun | Provides all you need to run the application in the configured servlet container, either normally (runApp/runAppHttps) or from a WAR file (runWar/runWarHttps). |
| スクリプト | 説明 |
|---|
| _GrailsSettings | Grailsの設定などを読み込むスクリプト。このスクリプトは他のスクリプト(_GrailsProxyなど)で自動的にインクルードされているので、通常は明示的にインクルードする必要はありません。 |
| _GrailsEvents | イベントトリガーを実装するためのメソッド(event(String eventName, List args))を使用するには、これをインクルードする必要があります。このスクリプトもほぼ全てのGrailsスクリプトでインクルードされています。 |
| _GrailsClasspath | コンパイル、テスト、およびランタイムのクラスパスを設定します。このスクリプトもほぼ全ての Grailsスクリプトでインクルードされています。 |
| _GrailsProxy | インターネットにアクセスする場合は、プロキシの解決をするためにこのスクリプトをインクルードして下さい。 |
| _GrailsArgParsing | parseArgumentsターゲットはその名の通り解析する機能を提供します。スクリプトを実行する際に指定した引数を解析します。argsMapプロパティにそれらの設定の追加します。 |
| _GrailsTest | すべてのテスト実行に使用するコードが含まれています。他の種類のテストを追加する際に便利です。 |
| _GrailsRun | アプリケーションを起動させるために必要な機能を提供します。通常は(runApp/runAppHttps)から、またはWARファイル(runWar/runWarHttps)から実行します。 |
There are many more scripts provided by Grails, so it is worth digging into the scripts themselves to find out what kind of targets are available. Anything that starts with an "_" is designed for reuse.
Grailsではもっと多くのスクリプトが提供されていますので、どんな種類のターゲットが利用可能かを調べてみる価値があるでしょう。"
"で始まっているものはすべて再利用されることを考慮してデザインされています。スクリプトアーキテクチャ
Script architecture
You maybe wondering what those underscores are doing in the names of the Grails scripts. That is Grails' way of determining that a script is _internal , or in other words that it has not corresponding "command". So you can't run "grails _grails-settings" for example. That is also why they don't have a default target.
アンダースコアで始まるGrailsスクリプトは、何を示しているものかを説明すると、それらはコマンドではなく、他のスクリプトから利用されるスクリプト群として認識されます。なので、それらのスクリプト(内部スクリプト)はデフォルトターゲットを持っておらず、スクリプトは実行できません。Internal scripts are all about code sharing and reuse. In fact, we recommend you take a similar approach in your own scripts: put all your targets into an internal script that can be easily shared, and provide simple command scripts that parse any command line arguments and delegate to the targets in the internal script. For example if you have a script that runs some functional tests, you can split it like this:
内部スクリプトは共有して再利用するために存在します。実際に独自のスクリプトを書く場合は、同等の手法をとることをお勧めします。簡単に共有できるターゲットは内部スクリプトにすべて置き、コマンドライン引数を解析して、内部スクリプト内のターゲットを呼び出すだけのコマンドスクリプトを提供します。例えば、いくつかのファンクショナルテストを行うスクリプトがあるという場合、以下のように分割できます。./scripts/FunctionalTests.groovy:includeTargets << new File("${basedir}/scripts/_FunctionalTests.groovy")target(default: "Runs the functional tests for this project.") {
depends(runFunctionalTests)
}./scripts/_FunctionalTests.groovy:includeTargets << grailsScript("_GrailsTest")target(runFunctionalTests: "Run functional tests.") {
depends(...)
…
}Here are a few general guidelines on writing scripts:
以下にスクリプトを書く際のガイドラインを示します:
- Split scripts into a "command" script and an internal one.
- Put the bulk of the implementation in the internal script.
- Put argument parsing into the "command" script.
- To pass arguments to a target, create some script variables and initialise them before calling the target.
- Avoid name clashes by using closures assigned to script variables instead of targets. You can then pass arguments direct to the closures.
- スクリプトを"コマンドスクリプト"と"内部スクリプト"に分割します。
- 実装の大部分は"内部スクリプト"で行います。
- 引数の解析は"コマンドスクリプト"で行います。
- ターゲットに引数を渡すには、いくつかのスクリプト変数を作成し、ターゲットを呼び出す前にそれらを初期化します。
- ターゲットの代わりにスクリプト変数に割り当てられているクロージャを使用して名前の衝突を避けるようにします。そうすれば、引数をクロージャに直接渡すことができます。
4.4 イベントを取得する
Grails provides the ability to hook into scripting events. These are events triggered during execution of Grails target and plugin scripts.
Grailsはスクリプトのイベントフックを提供しています。イベントフックとは、Grailsターゲット実行時やプラグインスクリプト実行時に発行されるイベントを取得して処理を行うことができる機能です。The mechanism is deliberately simple and loosely specified. The list of possible events is not fixed in any way, so it is possible to hook into events triggered by plugin scripts, for which there is no equivalent event in the core target scripts.
仕組みはわざと単純でゆるく明記できるようになっています。起こりうるイベントは予測できないからです。なので、コアターゲットと同等のイベントが無い場合はプラグインスクリプトからトリガーされたイベントにフックする事も可能です。イベントハンドラを定義する
Defining event handlers
Event handlers are defined in scripts called _Events.groovy. Grails searches for these scripts in the following locations:
イベントハンドラは_Events.groovyという名称のスクリプトで定義します。Grailsは次の場所からスクリプトを検索します:
USER_HOME/.grails/scripts - user-specific event handlersPROJECT_HOME/scripts - applicaton-specific event handlersPLUGINS_HOME/*/scripts - plugin-specific event handlersGLOBAL_PLUGINS_HOME/*/scripts - event handlers provided by global plugins
USER_HOME/.grails/scripts - ユーザー固有のイベントハンドラPROJECT_HOME/scripts - アプリケーション固有のイベントハンドラPLUGINS_HOME/*/scripts - プラグイン固有のイベントハンドラGLOBAL_PLUGINS_HOME/*/scripts - グローバルプラグインによって提供されているイベントハンドラ
Whenever an event is fired, all the registered handlers for that event are executed. Note that the registration of handlers is performed automatically by Grails, so you just need to declare them in the relevant _Events.groovy file.
イベントが発生するたびに登録されている すべての ハンドラが実行されます。ハンドラの登録はGrailsによって自動的に行われることに注意してください。なので、必要な作業は関連する_Events.groovyファイルにそれらを宣言するだけです。Event handlers are blocks defined in _Events.groovy, with a name beginning with "event". The following example can be put in your /scripts directory to demonstrate the feature:
イベントハンドラは _Events.groovy で定義されている名前が "event" で始まっているブロックです。次の例のように_Events.groovyを記述して、/scripts ディレクトリに配置することによって、イベントハンドラを実装することができます:eventCreatedArtefact = { type, name ->
println "Created $type $name"
}eventStatusUpdate = { msg ->
println msg
}eventStatusFinal = { msg ->
println msg
}You can see here the three handlers
eventCreatedArtefact,
eventStatusUpdate,
eventStatusFinal. Grails provides some standard events, which are documented in the command line reference guide. For example the
compile command fires the following events:
eventCreatedArtefact、eventStatusUpdate、eventStatusFinal。Grailsはいくつかの標準的なイベントを提供しています。詳細はコマンドラインリファレンスガイドを参照してください。たとえば、 compileコマンドは、次のようなイベントを発行させます。
CompileStart - Called when compilation starts, passing the kind of compile - source or testsCompileEnd - Called when compilation is finished, passing the kind of compile - source or tests
CompileStart - sourceまたはtestsコンパイル開始時に発行されます。CompileEnd - sourceまたはtestsコンパイル終了時に発行されます。
イベントトリガー
Triggering events
To trigger an event simply include the Init.groovy script and call the event() closure:
イベントを発行するには _GrailsEvents.groovy スクリプトをインクルードしてevent()クロージャを使用します:includeTargets << grailsScript("_GrailsEvents")event("StatusFinal", ["Super duper plugin action complete!"])共通イベント
Common Events
Below is a table of some of the common events that can be leveraged:
以下はいくつかの利用可能な共通イベントの一覧です:
| Event | Parameters | Description |
|---|
| StatusUpdate | message | Passed a string indicating current script status/progress |
| StatusError | message | Passed a string indicating an error message from the current script |
| StatusFinal | message | Passed a string indicating the final script status message, i.e. when completing a target, even if the target does not exit the scripting environment |
| CreatedArtefact | artefactType,artefactName | Called when a create-xxxx script has completed and created an artefact |
| CreatedFile | fileName | Called whenever a project source filed is created, not including files constantly managed by Grails |
| Exiting | returnCode | Called when the scripting environment is about to exit cleanly |
| PluginInstalled | pluginName | Called after a plugin has been installed |
| CompileStart | kind | Called when compilation starts, passing the kind of compile - source or tests |
| CompileEnd | kind | Called when compilation is finished, passing the kind of compile - source or tests |
| DocStart | kind | Called when documentation generation is about to start - javadoc or groovydoc |
| DocEnd | kind | Called when documentation generation has ended - javadoc or groovydoc |
| SetClasspath | rootLoader | Called during classpath initialization so plugins can augment the classpath with rootLoader.addURL(...). Note that this augments the classpath after event scripts are loaded so you cannot use this to load a class that your event script needs to import, although you can do this if you load the class by name. |
| PackagingEnd | none | Called at the end of packaging (which is called prior to the Tomcat server being started and after web.xml is generated) |
| イベント | パラメータ | 説明 |
|---|
| StatusUpdate | message | 実行されているスクリプトのステータス、進捗メッセージを知らせる |
| StatusError | message | 実行されているスクリプトのエラーメッセージを 知らせる |
| StatusFinal | message | スクリプトの終了時に最終メッセージを知らせる。 スクリプトによっては完全終了時ではなく、コマ ンドの終了時に動作する |
| CreatedArtefact | artefactType,artefactName | create-xxxxなどのアーティファクト生成スクリプトが、アーティファクトの生成完了時にアーティ ファクトタイプとアーティファクト名を知らせる |
| CreatedFile | fileName | ファイルがスクリプトによって生成されたときに ファイル名を知らせる |
| Exiting | returnCode | スクリプトが正常に終了したときに終了コードを 知らせる |
| PluginInstalled | pluginName | プラグインのインストールが終了した後にプラグイン 名を知らせる |
| CompileStart | kind | コンパイル開始時にコンパイルする種類(source または tests)を知らせる |
| CompileEnd | kind | コンパイル終了時にコンパイルした種類(source または tests)を知らせる |
| DocStart | kind | ドキュメント生成時に、どのドキュメント生成(javadoc または groovydoc)が開始するかを知らせる |
| DocEnd | kind | ドキュメント生成完了時に、どのドキュメント生成(javadoc または groovydoc)が完了したかを知らせる |
| SetClasspath | rootLoader | クラスパス初期化中にGrailsRootLoader が渡されるので、「rootLoader.addURL( … )」でクラスをGrailsRootLoader に追加できる |
| PackagingEnd | none | Grailsアプリケーションのパッケージング完了時 (web.xml生成後、Tomcatサーバ起動前)に呼び出される |
4.5 ビルドのカスタマイズ
Grails is most definitely an opinionated framework and it prefers convention to configuration, but this doesn't mean you can't configure it. In this section, we look at how you can influence and modify the standard Grails build.
Grailsは確かにものすごく固執したフレームワークであり、設定よりも規約という方式を主張していますが、それは様々な設定をできないという意味ではありません。このセクションでは、どのようにGrailsの標準的なビルドをカスタマイズする方法を解説します。初期値
The defaults
The core of the Grails build configuration is the grails.util.BuildSettings class, which contains quite a bit of useful information. It controls where classes are compiled to, what dependencies the application has, and other such settings.
ビルド設定の中心部分は、ビルド時に有用な情報が含まれている grails.util.BuildSettingsクラスです。このクラスは、どこにコンパイルされるのか、アプリケーションが何に依存関係を持っているのか、どのような設定を保持しているのか、を制御します。Here is a selection of the configuration options and their default values:
設定オプションと初期値は以下のようになります:
| Property | Config option | Default value |
|---|
| grailsWorkDir | grails.work.dir | $USER_HOME/.grails/<grailsVersion> |
| projectWorkDir | grails.project.work.dir | <grailsWorkDir>/projects/<baseDirName> |
| classesDir | grails.project.class.dir | <projectWorkDir>/classes |
| testClassesDir | grails.project.test.class.dir | <projectWorkDir>/test-classes |
| testReportsDir | grails.project.test.reports.dir | <projectWorkDir>/test/reports |
| resourcesDir | grails.project.resource.dir | <projectWorkDir>/resources |
| projectPluginsDir | grails.project.plugins.dir | <projectWorkDir>/plugins |
| globalPluginsDir | grails.global.plugins.dir | <grailsWorkDir>/global-plugins |
| verboseCompile | grails.project.compile.verbose | false |
| プロパティ | 設定オプション | 初期値 |
|---|
| grailsWorkDir | grails.work.dir | $USER_HOME/.grails/<grailsVersion> |
| projectWorkDir | grails.project.work.dir | <grailsWorkDir>/projects/<baseDirName> |
| classesDir | grails.project.class.dir | <projectWorkDir>/classes |
| testClassesDir | grails.project.test.class.dir | <projectWorkDir>/test-classes |
| testReportsDir | grails.project.test.reports.dir | <projectWorkDir>/test/reports |
| resourcesDir | grails.project.resource.dir | <projectWorkDir>/resources |
| projectPluginsDir | grails.project.plugins.dir | <projectWorkDir>/plugins |
| globalPluginsDir | grails.global.plugins.dir | <grailsWorkDir>/global-plugins |
| verboseCompile | grails.project.compile.verbose | false |
The BuildSettings class has some other properties too, but they should be treated as read-only:
BuildSettingsクラスは、他にもいくつかの読み取り専用のプロパティを持っています:
| Property | Description |
|---|
| baseDir | The location of the project. |
| userHome | The user's home directory. |
| grailsHome | The location of the Grails installation in use (may be null). |
| grailsVersion | The version of Grails being used by the project. |
| grailsEnv | The current Grails environment. |
| compileDependencies | A list of compile-time project dependencies as File instances. |
| testDependencies | A list of test-time project dependencies as File instances. |
| runtimeDependencies | A list of runtime-time project dependencies as File instances. |
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|
| baseDir | プロジェクトの場所。 |
| userHome | ユーザーのホームディレクトリ。 |
| grailsHome | 使用中のGrailsのインストール先(nullの場合あり)。 |
| grailsVersion | プロジェクトで使用されているGrailsのバージョン。 |
| grailsEnv | 現在のGrails環境。 |
| compileDependencies | コンパイル時のプロジェクト依存関係のFileインスタンスのリスト。 |
| testDependencies | テスト時のプロジェクト依存関係のFileインスタンスのリスト。 |
| runtimeDependencies | 実行時のプロジェクト依存関係のFileインスタンスのリスト。 |
Of course, these properties aren't much good if you can't get hold of them. Fortunately that's easy to do: an instance of BuildSettings is available to your scripts as the grailsSettings script variable. You can also access it from your code by using the grails.util.BuildSettingsHolder class, but this isn't recommended.
もちろんこれらのプロパティがぴったり合うとは限りません。幸いなことに、BuildSettingsのインスタンスのgrailsSettingspスクリプト変数を介して利用可能です。他のコードからもgrails.util.BuildSettingsHolder@クラスを使用してアクセスすることができます。でもこれは推奨されません。初期値を上書きする
Overriding the defaults
All of the properties in the first table can be overridden by a system property or a configuration option - simply use the "config option" name. For example, to change the project working directory, you could either run this command:
1つめの表内のすべてのプロパティは、システムプロパティや設定オプションで上書きすることができます。たとえば、プロジェクトの作業ディレクトリ(projectWorkDir)を変更するには、このようにコマンドを実行することができます:
grails -Dgrails.project.work.dir=work compile
or add this option to your grails-app/conf/BuildConfig.groovy file:
grails-app/conf/BuildConfig.groovyに記述します:
grails.project.work.dir = "work"
Note that the default values take account of the property values they depend on, so setting the project working directory like this would also relocate the compiled classes, test classes, resources, and plugins.
注意点として、プロパティが依存しているプロパティのデフォルト値にも影響するので、このようにプロジェクトの作業ディレクトリを設定すると、コンパイルされたクラス、テストクラス、リソース、およびプラグインの場所を変更することにもなります。What happens if you use both a system property and a configuration option? Then the system property wins because it takes precedence over the BuildConfig.groovy file, which in turn takes precedence over the default values.
システムプロパティと設定オプションの両方を指定した場合、システムプロパティはBuildConfig.groovyファイルの設定よりも優先順位が高いので、システムプロパティの値が設定されます。The BuildConfig.groovy file is a sibling of grails-app/conf/Config.groovy - the former contains options that only affect the build, whereas the latter contains those that affect the application at runtime. It's not limited to the options in the first table either: you will find build configuration options dotted around the documentation, such as ones for specifying the port that the embedded servlet container runs on or for determining what files get packaged in the WAR file.
BuildConfig.groovyファイルは、grails-app/conf/Config.groovyと兄妹関係にあります。前者は、ビルド時にのみ影響を及ぼすオプションを含んでいるのに対して、後者はアプリケーションの実行時に影響を与えるオプションを含んでいます。設定オプションは、1つめの表で示したオプション以外にも、サーブレットコンテナを動かすポート指定や、WARファイルにどのファイルを格納するかを決定する指定など、他にも指定可能なビルド設定が存在します。使用可能なビルド設定
Available build settings
| Name | Description |
|---|
| grails.server.port.http | Port to run the embedded servlet container on ("run-app" and "run-war"). Integer. |
| grails.server.port.https | Port to run the embedded servlet container on for HTTPS ("run-app --https" and "run-war --https"). Integer. |
| grails.config.base.webXml | Path to a custom web.xml file to use for the application (alternative to using the web.xml template). |
| grails.compiler.dependencies | Legacy approach to adding extra dependencies to the compiler classpath. Set it to a closure containing "fileset()" entries. These entries will be processed by an AntBuilder so the syntax is the Groovy form of the corresponding XML elements in an Ant build file, e.g. fileset(dir: "$basedir/lib", include: "**/*.class). |
| grails.testing.patterns | A list of Ant path patterns that let you control which files are included in the tests. The patterns should not include the test case suffix, which is set by the next property. |
| grails.testing.nameSuffix | By default, tests are assumed to have a suffix of "Tests". You can change it to anything you like but setting this option. For example, another common suffix is "Test". |
| grails.project.war.file | A string containing the file path of the generated WAR file, along with its full name (include extension). For example, "target/my-app.war". |
| grails.war.dependencies | A closure containing "fileset()" entries that allows you complete control over what goes in the WAR's "WEB-INF/lib" directory. |
| grails.war.copyToWebApp | A closure containing "fileset()" entries that allows you complete control over what goes in the root of the WAR. It overrides the default behaviour of including everything under "web-app". |
| grails.war.resources | A closure that takes the location of the staging directory as its first argument. You can use any Ant tasks to do anything you like. It is typically used to remove files from the staging directory before that directory is jar'd up into a WAR. |
| grails.project.web.xml | The location to generate Grails' web.xml to |
| 名前 | 説明 |
|---|
| grails.server.port.http | 組み込みのサーブレットコンテナを実行するポート番号。("run-app" と "run-war") |
| grails.server.port.https | HTTPS用の組み込みのサーブレットコンテナを実行するポート番号。("run-app --https"と"run-war --https") |
| grails.config.base.webXml | アプリケーションで使用するカスタムのweb.xmlファイルへのパス。(web.xmlテンプレートを使用しない場合) |
| grails.compiler.dependencies | コンパイラのクラスパスに依存関係を追加する。"fileset()"を含んでいるクロージャに設定。 |
| grails.testing.patterns | テストに含まれるファイルを制御するためのAntパスのパターンリスト。パターンは、次のgrails.testing.nameSuffixに設定されているテストケースのサフィックス以外。 |
| grails.testing.nameSuffix | デフォルトでは、テストは"Tests"のサフィックスが設定されていますが、好きなようにオプション設定を変更することができます。 |
| grails.project.war.file | 生成されるWARファイルの名称(拡張子を含む)のファイルパス。例として、"target/my-app.war" 等。 |
| grails.war.dependencies | WARファイルの"WEB-INF/lib"階層に含む内容を、クロージャ内の"fileset()"でコントロール。 |
| grails.war.copyToWebApp | WARのルートディレクトリ階層に含む内容を、クロージャ内の"fileset()"でコントロール。 |
| grails.war.resources | 最初の引数としてステージングディレクトリの場所を受け取れるクロージャを指定。クロージャ内でAntタスクを使用することで、WAR化される前にステージングディレクトリの内容を変更する事ができます。 |
| grails.project.web.xml | Grailsがweb.xmlを生成する場所の指定。 |
4.6 AntとMaven
If all the other projects in your team or company are built using a standard build tool such as Ant or Maven, you become the black sheep of the family when you use the Grails command line to build your application. Fortunately, you can easily integrate the Grails build system into the main build tools in use today (well, the ones in use in Java projects at least).
もし、あなたのプロジェクトチームや会社でAntやMavenなどのような標準的なビルドツールを利用している場合は、アプリケーションをビルドする時にGrailsのコマンドラインを使っていると一家の厄介者にされてしまいます。幸いなことに、Grailsビルドシステムは今日使われている主なビルドツールに簡単に統合することができます。(少なくともJavaプロジェクトで使用されているものへ)Antへの統合
Ant Integration
When you create a Grails application with the
create-app command, Grails doesn't automatically create an Ant
build.xml file but you can generate one with the
integrate-with command:
build.xmlを生成しません。integrate-withコマンドを使用して生成することが可能です。
grails integrate-with --ant
This creates a build.xml file containing the following targets:
作成されたbuild.xmlファイルには、次のターゲットが含まれています:
clean - Cleans the Grails applicationcompile - Compiles your application's source codetest - Runs the unit testsrun - Equivalent to "grails run-app"war - Creates a WAR filedeploy - Empty by default, but can be used to implement automatic deployment
clean - Grailsアプリケーションをクリーンします。compile - アプリケーションのソースコードをコンパイルします。test - Unitテストを実行します。run - Grailsの"run-app"コマンド相当を実行します。war - WARファイルを作成します。deploy - デフォルトでは空ですが、自動配備を実装することができます。
Each of these can be run by Ant, for example:
これらは例えば、以下のようなAntコマンドで実行できます。The build file is configured to use
Apache Ivy for dependency management, which means that it will automatically download all the requisite Grails JAR files and other dependencies on demand. You don't even have to install Grails locally to use it! That makes it particularly useful for continuous integration systems such as
CruiseControl or
Jenkins.
It uses the Grails
Ant task to hook into the existing Grails build system. The task lets you run any Grails script that's available, not just the ones used by the generated build file. To use the task, you must first declare it:
<taskdef name="grailsTask"
classname="grails.ant.GrailsTask"
classpathref="grails.classpath"/>This raises the question: what should be in "grails.classpath"? The task itself is in the "grails-bootstrap" JAR artifact, so that needs to be on the classpath at least. You should also include the "groovy-all" JAR. With the task defined, you just need to use it! The following table shows you what attributes are available:
ここで疑問が生じます。どれが"grails.classpath"でしょうか。タスク自体は"grails-bootstrap"JARの一部です。なので、少なくともクラスパス上にある必要があります。また、"groovy-all" JARを含める必要があります。タスク宣言ではこれらを仕使用する必要があります!次の表は、どんな属性が利用可能かを示しています。
| Attribute | Description | Required |
|---|
| home | The location of the Grails installation directory to use for the build. | Yes, unless classpath is specified. |
| classpathref | Classpath to load Grails from. Must include the "grails-bootstrap" artifact and should include "grails-scripts". | Yes, unless home is set or you use a classpath element. |
| script | The name of the Grails script to run, e.g. "TestApp". | Yes. |
| args | The arguments to pass to the script, e.g. "-unit -xml". | No. Defaults to "". |
| environment | The Grails environment to run the script in. | No. Defaults to the script default. |
| includeRuntimeClasspath | Advanced setting: adds the application's runtime classpath to the build classpath if true. | No. Defaults to true. |
| 属性 | 説明 | 必須 |
|---|
| home | ビルドに使用するGrailsのインストールディレクトリの場所。 | パスが指定されている場合を除き必須です。 |
| classpathref | Grailsがロードする基点となるクラスパス。"grails-bootstrap"を含めなければなりません。また、"grails-scripts"を含めるべきです。 | homeが設定されていなかったり、classpath要素を使う場合は必須です。 |
| script | Grailsスクリプトの実行名。例えば "TestApp"。 | 必須です。 |
| args | スクリプトに渡す引数。例えば "-unix -xml"。 | 必須ではありません。デフォルトは "" です。 |
| environment | スクリプト実行時のGrails環境変数。 | 必須ではありません。デフォルトはスクリプトのデフォルトになります。 |
| includeRuntimeClasspath | 高度な設定です。 trueの場合、アプリケーション実行時クラスパスをクラスパスに追加します。 | 必須ではありません。 デフォルトはtrueです。 |
The task also supports the following nested elements, all of which are standard Ant path structures:
タスクネスト要素をサポートします。こられの全ては標準的なAntの構造となっています。
classpath - The build classpath (used to load Gant and the Grails scripts).compileClasspath - Classpath used to compile the application's classes.runtimeClasspath - Classpath used to run the application and package the WAR. Typically includes everything in @compileClasspath.testClasspath - Classpath used to compile and run the tests. Typically includes everything in runtimeClasspath.
classpath - ビルド時のクラスパス。(GantとGrailsスクリプトロード時に使用)compileClasspath - アプリケーションコンパイル時のクラスパス。runtimeClasspath - アプリケーションとWARパッケージ実行時のクラスパス。通常compileClasspathに全てが含まれます。testClasspath - コンパイル時と、テスト実行時のクラスパス。通常runtimeClasspathに全てが含まれます。
How you populate these paths is up to you. If you use the home attribute and put your own dependencies in the lib directory, then you don't even need to use any of them. For an example of their use, take a look at the generated Ant build file for new apps.
どうやってパスを追加するかはあなた次第です。もし、homeを利用しており、自分自身の依存関係をlibディレクトリに設定している場合は、これらを使う必要はありません。こららの利用例としては、生成された新しいアプリケーションのAntビルドファイルを見てみましょう。Mavenの統合
Maven Integration
Grails provides integration with
Maven 2 with a Maven plugin. The current Maven plugin is based on but supersedes the version created by
Octo, who did a great job with the original.
準備
Preparation
In order to use the new plugin, all you need is Maven 2 installed and set up. This is because you no longer need to install Grails separately to use it with Maven!
新しいプラグインを使用するのに必要なことは、Maven2をインストールし設定することです。なぜなら、Grailsを別途インストールする必要はないからです!
The Maven 2 integration for Grails has been designed and tested for Maven 2.0.9 and above. It will not work with earlier versions.
GrailsのMaven2統合は、Maven 2.0.9以上を対象として設計・テストされています。それ以前のバージョンでは動作しません。
The default mvn setup DOES NOT supply sufficient memory to run the Grails environment. We recommend that you add the following environment variable setting to prevent poor performance:
既定のmvnコマンド設定ではGrails環境で実行するための十分なメモリを供給できません。パフォーマンス低下を防止するため、次の環境変数を追加することをお勧めします:export MAVEN_OPTS="-Xmx512m -XX:MaxPermSize=256"
GrailsのMavenのプロジェクトを作成する
Creating a Grails Maven Project
To create a Mavenized Grails project simply run the following command:
Maven化されたGrailsプロジェクトを作成するには、単に以下のコマンドを実行します:mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=org.grails \
-DarchetypeArtifactId=grails-maven-archetype \
-DarchetypeVersion=1.3.2 \
-DgroupId=example -DartifactId=my-appChoose whichever grails version, group ID and artifact ID you want for your application, but everything else must be as written. This will create a new Maven project with a POM and a couple of other files. What you won't see is anything that looks like a Grails application. So, the next step is to create the project structure that you're used to.
アプリケーションで使用するGrailsバージョン、グループID、アーティファクトIDを指定するだけで必要な内容が書き込まれます。このコマンドで新規にMavenプロジェクトのPOMと他のファイルが生成されます。生成された内容を見るとGrailsアプリケーションで必要なものが見つかりません。次のステップでいつも通りの物が出来上がります。
But first, to set target JDK to Java 6, do that now. Open my-app/pom.xml and change
はじめに、ターゲットJDKをJava 6にセットします。my-app/pom.xmlを開いて、次のように変更します:
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.5</source>
<target>1.5</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>to
上記を、以下のように変更します。
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>Then you're ready to create the project structure:
これでプロジェクト構造を作成する環境が整いました。
if you see a message similar to this:
以下のようなメッセージが出る場合:Resolving plugin JAR dependencies …
:: problems summary ::
:::: WARNINGS
module not found: org.hibernate#hibernate-core;3.3.1.GAyou need to add the plugins manually to application.properties:
application.properties に手動でプラグインを追加する必要があります:plugins.hibernate=2.0.0
plugins.tomcat=2.0.0
then run
そして実行します。and the hibernate and tomcat plugins will be installed.
これで、hibernateとtomcatプラグインがインストールされます。
Now you have a Grails application all ready to go. The plugin integrates into the standard build cycle, so you can use the standard Maven phases to build and package your app: mvn clean , mvn compile , mvn test , mvn package , mvn install .
これで、Grailsアプリケーションのすべての準備が整いました。プラグインは標準ビルドサイクルに統合され、Mavenの標準的なアプリケーションのビルドやパッケージングのフェーズで利用できるようになります: mvn clean、mvn compile、mvn test、mvn package、mvn install。You can also use some of the Grails commands that have been wrapped as Maven goals:
また、MavenのゴールとしてラッピングされたGrailsコマンドを使うこともできるようになっています:
For a complete, up to date list, run mvn grails:help
完全なリストはmvn grails:helpで確認して下さい。既存プロジェクトをMaven化する
Mavenizing an existing project
Creating a new project is great way to start, but what if you already have one? You don't want to create a new project and then copy the contents of the old one over. The solution is to create a POM for the existing project using this Maven command (substitute the version number with the grails version of your existing project):
新しく始めるには、プロジェクトを新規作成するのが最善の方法ですが、既にプロジェクトが存在する場合はどうしたらいいでしょうか?新しくプロジェクトを作成したくないし、内容を上書きコピーもしたくないでしょう。解決策は以下のMavenコマンドを使用して既存プロジェクトにPOMファイルを作ることです。(バージョン番号は既存のGrailsプロジェクトのバージョンで置き換えて下さい)mvn org.grails:grails-maven-plugin:1.3.2:create-pom -DgroupId=com.mycompany
When this command has finished, you can immediately start using the standard phases, such as mvn package. Note that you have to specify a group ID when creating the POM.
コマンドが完了したら、すぐにmvn packageのような標準フェーズで使い始めることができます。POMファイルを作成する際はグループIDを指定する必要があることに注意してください。You may also want to set target JDK to Java 6; see above.
また、対象JDKバージョンをJDK6に設定したい場合は、上記を参照して下さい。Grailsコマンドをフェーズに追加する
Adding Grails commands to phases
The standard POM created for you by Grails already attaches the appropriate core Grails commands to their corresponding build phases, so "compile" goes in the "compile" phase and "war" goes in the "package" phase. That doesn't help though when you want to attach a plugin's command to a particular phase. The classic example is functional tests. How do you make sure that your functional tests (using which ever plugin you have decided on) are run during the "integration-test" phase?
Grailsが作成した標準のPOMファイルは、Grailsのビルドフェーズに対応したコアコマンドに適切に付属しています。"compile" は "compile"フェーズに、"war" は "package"フェーズに。特定のフェーズにプラグインコマンドを付属させたい場合には役立ちません。古典的な例は、機能テストです。どうやって機能テストが統合テストフェーズの間に(あなた使用しているどんなプラグインを使った場合でも)実行されるのかを確かめるのでしょうか?Fear not: all things are possible. In this case, you can associate the command to a phase using an extra "execution" block:
恐れる必要はありません、すべて可能です。この場合には、"execution"ブロックを追加してフェーズに関連付けることができます。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.grails</groupId>
<artifactId>grails-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
…
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>functional-tests</id>
<phase>integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>exec</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<command>functional-tests</command>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>This also demonstrates the grails:exec goal, which can be used to run any Grails command. Simply pass the name of the command as the command system property, and optionally specify the arguments with the args property:
またこれは grails:exec goal の実演にもなっています。Grailsのどんなコマンドも実行できるのです。単にコマンド名を渡すcommandシステムプロパティと、オプションで引数を渡すargsプロパティがあります:mvn grails:exec -Dcommand=create-webtest -Dargs=Book
GrailsのMavenプロジェクトのデバッグ
Debugging a Grails Maven Project
Maven can be launched in debug mode using the "mvnDebug" command. To launch your Grails application in debug, simply run:
Mavenは "mvnDebug" コマンドを使用して、デバッグモードで起動することができます。デバッグでGrailsアプリケーションを起動するには、単純に以下のコマンドを実行します:The process will be suspended on startup and listening for a debugger on port 8000.
プロセスは起動時に停止して、デバッガをポート8000上で待ち受けます。If you need more control of the debugger, this can be specified using the MAVEN_OPTS environment variable, and launch Maven with the default "mvn" command:
デバッガのより詳細に制御する必要がある場合は、環境変数のMAVEN_OPTSを指定して標準の "mvn" コマンドを使用してMavenを起動させます。MAVEN_OPTS="-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=5005"
mvn grails:run-app
問題提起
Raising issues
If you come across any problems with the Maven integration, please raise a JIRA issue as a sub-task of
GRAILS-3547.
 If you need to open a file whilst within interactive mode you can use the
If you need to open a file whilst within interactive mode you can use the  Even better, the
Even better, the  If you need to run an external process whilst interactive mode is running you can do so by starting the command with a !:
If you need to run an external process whilst interactive mode is running you can do so by starting the command with a !: Note that with ! (bang) commands, you get file path auto completion - ideal for external commands that operate on the file system such as 'ls', 'cat', 'git', etc.
Note that with ! (bang) commands, you get file path auto completion - ideal for external commands that operate on the file system such as 'ls', 'cat', 'git', etc.

